As the Indian financial sector is largely bank-centric, the performance of the banking sector is crucial in the development process of the economy. As per KPGM-CII report, India’s banking sector has the potential to become the fifth largest banking industry in the world by 2020. However, there are some serious threats this sector will be facing in the next 3-4 years. The article lists down the most important ones of them in detail.
High probability of decreasing trend in non-interest income: Non-interest income which is saving the banks during the tough times of limited credit growth is going to be under pressure once the small finance banks and payment banks become operational. According to a Neilsen report, more than 76% of the high and mid income groups would try the payment banks. This group which contributes to the online transactions and thus the commissions to the bank would shift to payment banks decreasing the income on transactions. So, do the shift in remittances and other non-banking services like small insurances etc., follow because of higher income rates to be offered by SFBs and payment banks. RBI considering giving licenses to formalise P2P channels is also a threat as this channel is a direct competitor to the micro-lending options of the bank.
Rising corporate debt market: With credit growth not moving in a desirable way (as shown in the Figure 1) over the few months, and a continued delay in the land and environmental clearances, there is no expectation of the growth revival in the nearest future. According to CRISIL, there is a significant scope to India’s debt market which is only nearly 17% of the GDP (compared to 123% of USA 77% of South Korea and compares poorly to many of the Asian emerging economies) [1] and the push from regulators like RBI and SEBI, the corporate in the near future would bypass the banks for their funding requirements. This would further decrease the lending portfolio for the banks and force them to look for alternatives.
Returns on G-Sec bonds: The government and the RBI have made financial inclusion as an agenda and gave licenses to the new banking entities like payment banks and small finance banks. Through this, the government brought a permanent customer for its debt. As payment banks park 75% of their deposits and SFBs park as per SLR requirements, the G-Sec bond’s demand increases and the cost decreases. This situation is expected to worsen further as the government is very committed on decreasing the overall fiscal deficit. 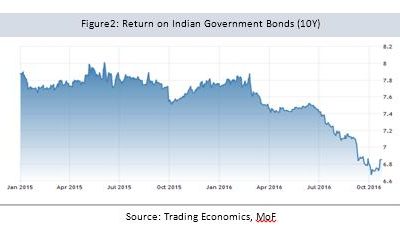
With limited avenues of lending, many banks including the private ones who invest in G-Sec’s (Most of the banks have SLR holdings of around 27-30% and State Bank of India slightly higher than 28%)[2] would lose a significant amount on their interest earnings thus decreasing the Net Interest Margin.
Alternative Avenues of Lending: With mounting Non-Performing Assets in public as well as private sector banks, the banks are increasingly focusing on retail and small business lending. However, these in a larger scale may not be a good alternative because of the limited knowledge on the credit history of such customers. Though the credit rating agencies have succeeded in providing credit ratings to the SMEs, the percentage of rating penetration is minuscule. The banks which struggle to complete their priority sector lending of 40% every year will find it very difficult to depend on this sector for higher lending. The banks now will also have to compete with the small finance banks (out of which most are Micro Finance Institutions) which have a 75% priority sector lending requirement who would target at Micro Small Medium Enterprises. The increased competition would result in lesser margins and thus impacting the returns of the banks as a whole.
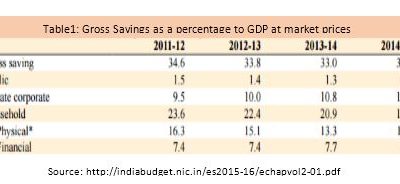
Increased cost of funds: As per the economic survey of 2015-16, the gross domestic savings rate in the economy declined by 1.6 percentage points of the GDP from 2011-12 to 2014-15. The marginal propensity to save (MPS) of the Indian consumers is gradually decreasing and is indicated in the decreasing trend of public savings in the table 1. Bandhan bank which
started offering as high as 8% will be followed by the SFBs and these would become the favourites of price sensitive Indian customers. With the above two factors, there would be a decrease in the value as well as the volume of the savings increasing the cost of funds for the banks.
Basel III as a danger: Though the implementation is set to be in 2019 and Indian banks are comfortably placed in many aspects (thanks top RBI’s conservative approach), the banks have to be prepared to phase out those instruments that are not allowed under Basel III. Increasing the quality of the marketable high liquid securities will actually make banks the customer for the corporate debt markets, giving more opportunities to the corporate.
All this at the time of investments: Last but not the least, the misfortune of the Indian banking sector combines with all the above as they have to make huge investments in technology to compete with their foreign counterparts who have already started making such investments.
Roadmap ahead: The time has come that the banks rethink their business model by concentrating more on niche markets and exploring new markets. Another way is to go digital, use the power of analytics to launch customised new products to retain the customer base and also increase their contribution to the banks.
-------------
About the Author:
Ms. Vaishnavi Adapa is a second year PGDM student at IIM Kozhikode. She has done her internship with CRISIL ratings.
