MBA admissions season is now on! Now that the results of CAT, XAT, SNAP and other entrance exams are out, GD-PI-WAT rounds are about to start. And this GD-PI-WAT season, one of the many things that the b-schools are searching for in candidates are - a) knowledge on current affairs, and b) their unique views on the matter and the ability to portray it in a clear and concise manner. You can only do that when you are aware and well-informed; specifically, about things happening in India and the world. A global event that has been in the spotlight for the better part of 2019 has been the US-China Trade War. The trade war is a big issue because the US and China are both economic superpowers. Whatever they do has an impact on the global economy (including India). So, what is this trade war all about?
What is the US-China Trade War?
It is a bitter trade battle between the two economic superpowers - the US and China. In 2018, US President Donald Trump began imposing tariffs and trade barriers on China. The reason behind this is the US's long formed suspicion on China's “unfair trade practices" and “intellectual property theft”. In retaliation, the Chinese government came up with its own tariffs. The graphic below captures the fundamental idea of the tariff escalation.
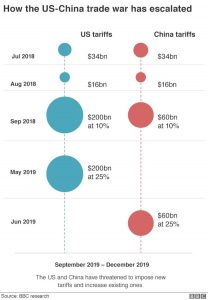
A Recap Of The Trade War
- In the year 1979, China opened its economy to foreign trade, investment and even started implementing free-market reforms. The world had great expectations from China (including the US).
- By 1988 China’s 15% of goods started being exported to the US.
- In 2001, China finally entered the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
- Since then the local spending power has already taken over America. And China started being termed as the 'world's factory’.
- There is also an increasing trade deficit with China. See the gap between imports and exports in the diagram below.
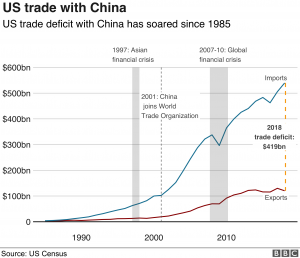 Source: BBC News
Source: BBC News - This made many nations (mostly US) believe that China has achieved economic growth by “not playing fair”.
- A secret investigation supported by the Trump administration revealed:
- There is a huge gap in import.
- The Chinese government treats Chinese companies differently, which means that If you decide to establish a business in China, your Chinese competition will have better access to the market and other benefits like granting lands for free or subsidised rate and gain tax break.
- There has also been a breach of Intellectual Property, especially with companies like Huawei.
The US Versus Huawei
America had imposed a ban on Huawei in the year 2019, with a 90 days grace period. But, it's not just really about the company but is, in fact, part of something bigger, and that is the US-China Tech/Trade War.
- In the rise of the trade war, the question of trusting Huawei (a company that is the world’s largest telecom equipment manufacturer) has been directly associated with trusting the Chinese government.
- Huawei increases its revenue through - handset manufacturing and electronics equipment manufacturing.
- It is the infrastructure side of the company that worries the government.
- Huawei, since 2018, has been trying to move forward and is a leading force in the 5G race.
- 5G strives for IoT (Internet of Things). Hence, the question of security poses a bigger issue as, in the hands of a hostile power, the entire network gets vulnerable to spying and illegal data tracking.
- Allegations on Huawei:
- Huawei sells its network at a cheaper price because they are heavily subsidised by the Chinese government.
- Huawei sells its network at a cheaper price because they are heavily subsidised by the Chinese government.
- If one buys Huawei equipment, they are exposed to surveillance by the Chinese intelligence services. This is due to the Chinese government act of 2017 - “Any organisation or citizen shall assist and cooperate with the state intelligence work.
Given Huawei's inability to stay independent, the relationship with the communist party, and their willingness to use hard power, there are suspicions that there can easily be situations where they can use 5G and intelligence from surveillance as an effective weapon. They can give a backdoor entry to the Chinese government to spy on its competitors and enemies.
Global Impact of the US-China Trade War
- If tariffs continue to expand and cover all US-China trade, then the markets will also see a dip. Global GDP might take a $600 billion hit in 2021, as predicted by Bloomberg economists Dan Hanson and Tom Orlik.
- The World Bank estimates the world economy will expand by only 2.6%. And the world GDP would plunge down to 0.9%, 0.7%, 0.6% or even lower in mid-2021.
- IMF has also predicted that the trade war could actually wipe $455 billion off the world’s GDP in 2020.
- The equity market drop will thus act as a further headwind to consumption and investment.
- The worst blows would be on South Korea, Malaysia and Taiwan if the drop in China’s exports to the U.S. continues.
- A trade war that keeps on escalating would impact foreign exchange markets through multiple channels: shifting trade flows, as well as expectations on growth and monetary policy.
US-China Trade War - Impact On India
- In the first half of 2019, India has been able to gain about $755 Million additional exports in chemicals, metals and ore, to the US.
- The imposition of US tariffs on China has made other countries more competitive in the US market. This led to something called a trade diversion effect. This diversion has benefited Korea, Canada and India in a smaller and substantial way - ranging from $0.9 - $1.5 billion.
- Indian adoption of non-alignment policy during the era of the Cold War has saved India from the counter effects of the trade war as compared to other economies. India maintains economic and diplomatic relations with both countries.
- Due to the US’s protectionist and unilateral policies, China and India have become more inclined towards a multilateral world. China could, therefore, form a relationship with India as a substitute.
- In fact, there is a fair chance that China could open up its markets for Indian goods and services – so could the US.
Trade War - Recent Developments
On 15th January 2020, US and China finally signed the phase 1 trade deal, easing the 1.6 years of trade tensions between the super-economies. The phase 1 deal will reduce US tariffs and boost China’s purchase of US goods. China has also agreed to purchase an additional US$200 billion worth of US goods and services over the next two years. This includes:
- Additional manufactured goods - US$ 78 billion
- Additional energy purchases - US$ 54 billion
- Additional farm products purchases - US$ 32 billion
- US$ 38 billion worth of other services
However, issues long-disputed on intellectual property, technology transfer, currency, and foreign exchange are still to be discussed. There could be a possible phase 2 trade deal related to that. But, the success of such a deal is uncertain.
Important Questions To Expect In The GD-PI-WAT Process
- Between the US or China, who is actually paying for the tariffs? Who bears the economic cost?
- What is the impact of the US-China trade war on consumers around the world?
- Will there be a contagious effect because of the ban on Huawei on American companies like Qualcomm, Intel and Qorvo?
- Does China have a trade deficit with any nation?
- Does the policy of limiting trade by imposing prohibitive tariffs and protectionism instruments of current trade wars lead to such a serious economic slowdown and a global economic crisis?
Resources
- U.S. China Trade War Explained: How Tariffs Work & Impact the Economy
- Is America right to fear Huawei? | The Economist
- The US-China Trade War: A Timeline
- China’s Economic Rise: History, Trends, Challenges, and Implications for the United States
- US vs Huawei: What is the controversy all about?
- America v China: why the trade war won't end soon | The Economist
- Semiconductors at the Heart of the US-China Tech War
- The Huawei controversy timeline: Everything you need to know!
- The US-China trade war has set in motion an unstoppable global economic transformation
- The U.S. – China Trade War: The Global Economic Fallout
- US-China Trade War And Its Global Impact
- A $600 Billion Bill: Counting the Global | Cost of the U.S.-China Trade War
- Explained: How The US-China Trade War Will Impact India
***
Coronavirus And Its Impact On Global Economy
Budget 2020 Analysis
Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA)
Iran USA Conflict
Article 370 And Article 35A
Venezuela's Oily Hyperinflation Story
The Zomato-Uber Eats Deal Explained
Why Should India Be Friends With Its Neighbours?
All You Need To Know About Air India
Opting Out Of RCEP - Does India Need To Rethink Its Decision?
